Maintaining good eye health is crucial, especially as we age. One eye condition that often sparks concern is glaucoma—a group of eye diseases that can lead to vision loss and blindness. But can an optometrist diagnose glaucoma? The answer is yes, and here’s how.
Understanding Glaucoma
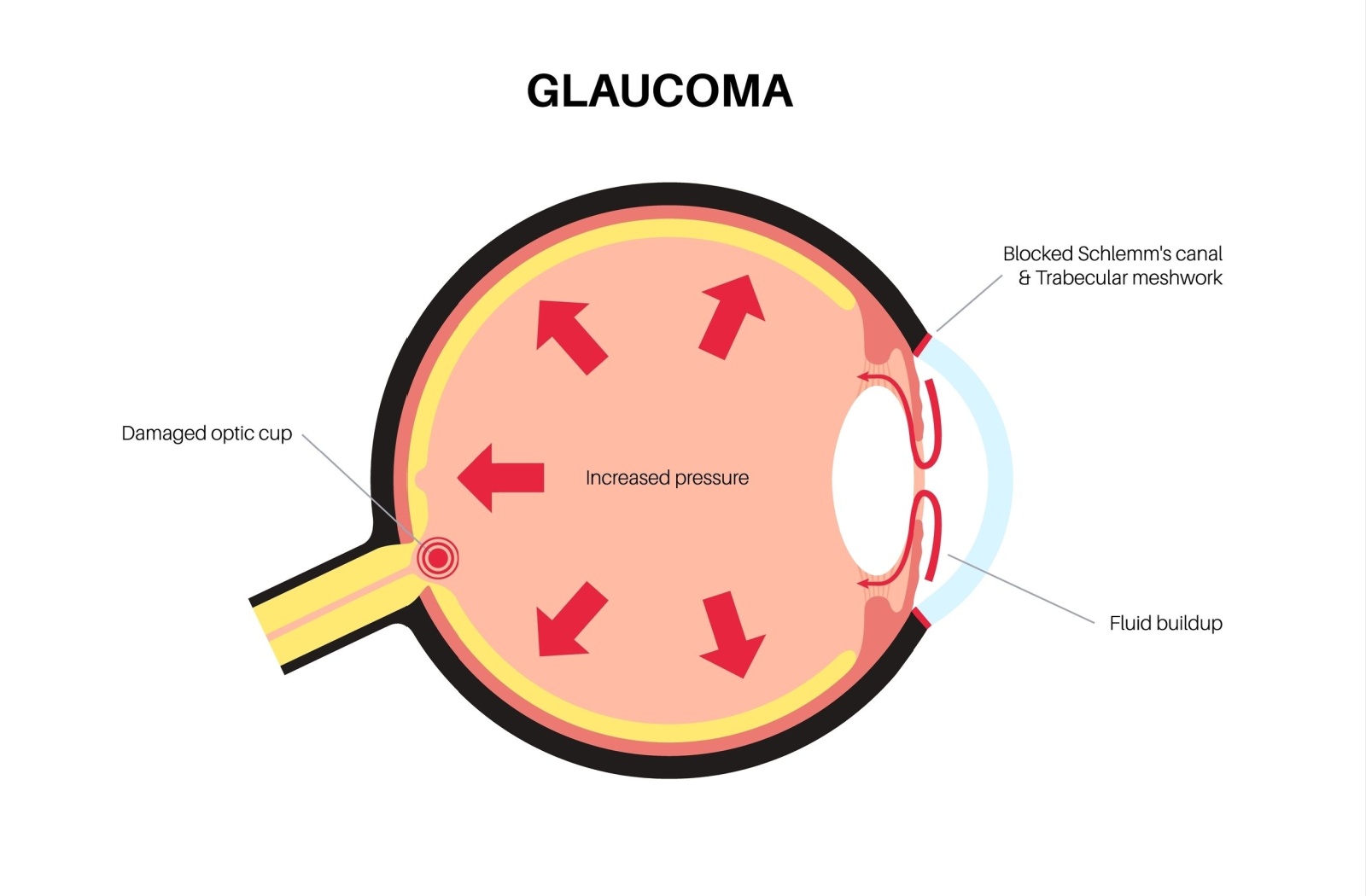
Glaucoma primarily affects the optic nerve, which is vital for good vision. This condition usually occurs when fluid builds up in the front part of the eye, increasing the pressure inside. The added pressure, known as intraocular pressure, can gradually damage the optic nerve over time, leading to vision loss.
Open-Angle Glaucoma: The most common form, where the drainage angle formed by the cornea and iris remains open, but the trabecular meshwork is partially blocked.
Glaucoma can develop slowly without noticeable symptoms, which is why it’s often called the “silent thief of sight.” Regular eye exams are crucial for early detection and management. There are several types of glaucoma, but the two main types are:
- Open-angle glaucoma: This is the most common form and occurs when the drainage canals in the eye become clogged over time.
- Angle-closure glaucoma: This is less common but can occur suddenly and is a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment.
Both types can lead to permanent vision loss if not properly managed. Early diagnosis and treatment can help preserve vision and prevent further damage.
- Angle-Closure Glaucoma: Less common but more severe, this type occurs when the iris bulges forward to narrow or block the drainage angle.
The Role of an Optometrist
Optometrists are healthcare professionals who provide primary vision care. This includes sight testing and correction, as well as the diagnosis, treatment, and management of vision changes. They are well-equipped to perform comprehensive eye exams that can identify early signs of glaucoma. Additionally, optometrists can prescribe eyeglasses and contact lenses, offer pre- and post-operative care for patients undergoing eye surgeries, and manage conditions like dry eye syndrome and macular degeneration. They play a crucial role in maintaining ocular health and ensuring patients have the best possible vision.
How Optometrists Diagnose Glaucoma
To diagnose glaucoma, optometrists use a variety of tests and techniques:
- Tonometry: This test measures the pressure inside the eye. Elevated intraocular pressure is a significant risk factor for glaucoma.
- Ophthalmoscopy: Using a special instrument, the optometrist examines the shape and color of the optic nerve.
- Perimetry (Visual Field Test): This test maps out your complete field of vision to determine if glaucoma is affecting your sight.
- Pachymetry: Measures the thickness of your cornea. Corneal thickness can influence eye pressure readings.
- Gonioscopy: This test inspects the drainage angle of the eye. It helps differentiate between open-angle and angle-closure glaucoma.
- Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT): A non-invasive imaging test that captures detailed images of the optic nerve and layers of the retina.
Early Detection is Key
Early detection of glaucoma is crucial for preventing vision loss, as this eye disease often progresses without noticeable symptoms. Regular eye exams can catch the disease in its early stages, even before any signs become apparent. This proactive approach allows for timely treatment, which can significantly slow the progression of the disease and preserve vision. This is particularly important for adults and seniors, who are at a higher risk for developing glaucoma due to factors such as age, family history, and certain medical conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure. By making eye health a priority and scheduling routine check-ups, individuals can take an important step in safeguarding their vision for the future.
Follow-Up and Treatment
If an optometrist suspects glaucoma, they may refer you to an ophthalmologist for further evaluation and treatment. During the evaluation, the ophthalmologist will conduct several tests to determine the extent of the condition. Treatment for glaucoma often includes prescription eye drops to reduce intraocular pressure, oral medications to enhance fluid drainage, laser treatment to improve fluid outflow, or surgery to create a new drainage pathway. The goal of these treatments is to lower the intraocular pressure and prevent further damage to the optic nerve, thereby preserving vision and preventing blindness. It is crucial to follow the prescribed treatment plan and attend regular follow-up appointments to monitor the condition effectively.
Importance of Regular Eye Exams
Whether you’re an eye care enthusiast or someone who hasn’t had an eye exam in years, it’s essential to understand the importance of regular check-ups. These evaluations are not just for maintaining your vision but also for your overall eye health. Adults and seniors should have comprehensive eye exams at least once a year. These exams are your first line of defense against glaucoma and other eye conditions such as cataracts, macular degeneration, and diabetic retinopathy. Early detection through regular check-ups can prevent serious vision loss and help maintain your quality of life. Remember, taking care of your eyes is as crucial as taking care of any other part of your body.
The Relationship Between Optometrists & Diagnosis
Optometrists play a vital role in diagnosing glaucoma. Through comprehensive eye exams and various diagnostic tests, they can detect early signs of the disease, making timely treatment possible. Prioritizing regular eye exams is a significant step in maintaining your eye health and preventing vision loss.
Are you due for an eye exam? Book an appointment with Broadway Eyecare today and take the first step towards safeguarding your vision.